National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (hereinafter referred to as "AIST") Geo-Chemistry Research Group, Geo-Resources and Environment Research Institute Research Group Leader Tetsuo Hodaka, Artificial Intelligence Research Center Social Intelligence Research Team Onishi Masateru Research Team Leader, Yoshiaki Bando Researcher, Wataru Naito Research Group Leader, Yuichi Iwasaki Senior Researcher, Naohide Shinohara Senior Researcher, Risk Assessment Strategy Group, Safety Science Research Division, Japan Football Association (JFA), Japan Professional Football League ( In collaboration with Nagoya Grampus, Yokohama F. Marinos, Vissel Kobe, Urawa Red Diamonds, and Kawasaki Frontale, the government, JFA, and J. We are promoting surveys and research on the implementation status of infection prevention measures such as evaluating the mask wearing rate by image recognition, and released a preliminary report for one game on October 11, 2021.
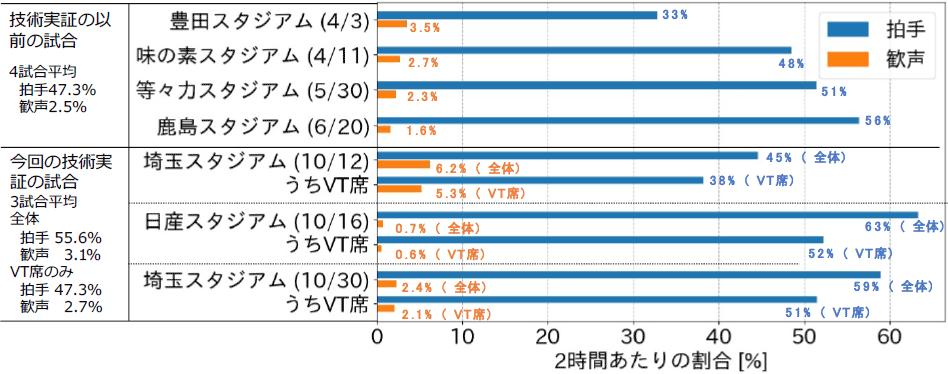
This time, the time required to pass through the check booth for vaccination certificates and negative certificates measured by laser radar, the mask wearing rate by image recognition, and the voice survey by microphone array of the 8 games held in October. We also report on the evaluation of the effect of infection risk control in stadiums based on the data obtained so far.
It was confirmed that the average confirmation time at the check booth for vaccination certificates and negative certificates was about 34 seconds. Regarding the mask-wearing rate, at the stadium where spectators actually entered, image recognition using artificial intelligence (AI) technology revealed that the mask-wearing rate during the match (other than halftime) was based on vaccine inspection package seats with certificates. It was calculated to be 93% and 95% for normal seats, confirming that there is no big difference. A speech survey using a microphone array revealed that the main type of cheering was applause, and the applause rate averaged 50.8% during the first two hours of the match. In addition, the percentage of time that a large number of people cheered at the audience's chance, etc. was 2.8% on average, and no significant difference was confirmed between the vaccine test package seats and the regular seats.
In addition, as an initiative outside the framework of this technology demonstration by the government, AIST can work with the research team MARCO to consider the infection prevention effect of vaccines in a spectator infection risk assessment model at a soccer stadium. The risk of infection was independently evaluated using parameters such as the mask wearing rate obtained from this technical demonstration. As a result, if the organizers and spectators work together to take measures, such as securing seat intervals, wearing masks, disinfecting, and washing hands, the risk of infection is 97% higher than if no measures were taken. rated as reduced. Furthermore, when taking into account the preventive effect of vaccines such as the introduction of VT sheets, the risk of infection is further reduced, estimated to be reduced by 98-98.5%. The results obtained this time are expected to contribute to the evaluation of the effects of infection prevention measures implemented at large-scale events such as stadiums, and to the evaluation of new coronavirus infection risk and evaluation of countermeasures, such as the creation of guidelines for countermeasures. .






![Advantages of "Gravio" that can implement face / person recognition AI with no code [Archive distribution now]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_6/2022/2/25/98ceaf1a66144152b81298720929e8e7.jpeg)